The relation between Bulk Modulus and Youngs Modulus. For example the value of K for steel is 161011 Nm2 and the value of K for glass is 410 10 Nm 2.
/young-woman-squeezing-stress-ball-against-white-background-1034879974-5ba0ee9fc9e77c0025d79d11.jpg)
What Is Bulk Modulus Definition Formulas Examples
This statement is valid only in the case of fluids not for solid.
/young-woman-squeezing-stress-ball-against-white-background-1034879974-5ba0ee9fc9e77c0025d79d11.jpg)
Bulk modulus k is defined as a ratio of. Youngs Modulus Stress Strain. The simplest isothermal EOS is the definition for incompressibility bulk modulus. In response to the hydrostatic load the specimen will change its volume.
Hooks law is used for defining which of the followinga Elastic limitb Stressc Straind Modulus of elasticity. From the equation if pressure increase volume decrease and the opposite if pressure decrease volume will expand in a vacuum but in some limit. Applied Dimensional Analysis and Modeling Second Edition 2007.
Using infinitesimal strain theory integration of K yields an EOS which implies that material is infinitely compressible which we know is not the case. Bulk modulus of elasticity K. As we know the formula for Bulk Modulus K.
Bulk modulus of elasticity of a substance is basically defined as the ratio of compressive stress or hydro static stress to volumetric strain and it will be displayed by the symbol K. Kf 1 cf. Bulk modulus is used to measure how incompressible a solid is.
P K ΔVV K PΔVV Where K Bulk modulus. Relation between young modulus and bulk modulus of materials is given as. It is the ratio of tangential stress to shearing strain.
The ratio of shear stress to shear strain. SI unit of the bulk modulus is the same as that of pressure ie Nm2 or Pa. B is the bulk modulus.
The ratio of volumetric stress to volume strain. Thus when KY 1-2sigma13. As given values in the problem.
The modulus ratio is given by A material has modulus of rigidity equal to 04x105 Nmm2 and Bulk modulus equal to 095 x105 Nmm2 The Youngs modulus value in GPa is. It is reciprocal of the compressibility of the fluid. 4 10 4 Nmm 2.
Technically K is defined as the ratio of hydrostatic pressure to the relative volume change which is related to the direct strains. Bulk Modulus K Atmosphere Technical Attopascal Bar Barye Centimeter Mercury 0C Centimeter Water 4C Centipascal Decapascal Decipascal Dyne per Square Centimeter Exapascal Femtopascal Foot Sea Water 15C Foot Water 4C Foot Water 60F Gigapascal Gram. β K d P d V V 1 β.
It describes the linear stress and strain whereas the bulk modulus defines the volumetric stresses and strain. Two materials are having modulus of elasticity modulus of rigidities and bulk modulus as E1 E2 C1 C2 and K1 K2. Therefore K must vary with P the more compressed matter is the harder it is.
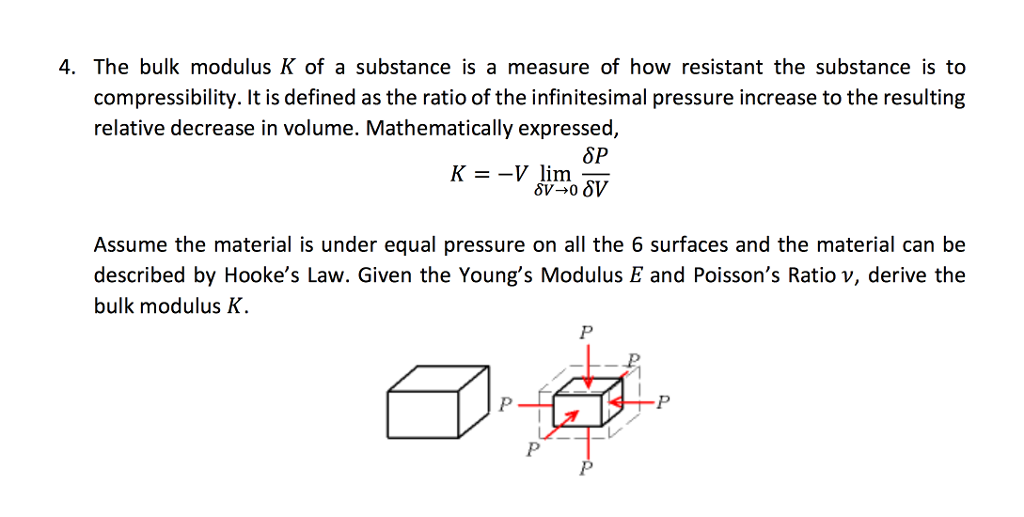
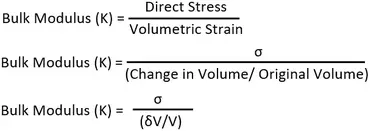
Besides the more the value of K for a material the higher is its nature to be incompressible. The Bulk modulus is defined as the ratio of direct stress to volumetric strain. The Bulk Modulus is defined as the ratio of the infinitesimal pressure increase to the resulting relative decrease of the volume.
Bulk modulus of a substance provides the information about the resistance of substance to the uniform pressure. For a mixture fluid compressibility can be estimated from a volume average of the phase compressibilities co cw cg thus cf coSo cwSw cgSg for an immiscible oil water and gas mixture. However principal stress acting in one direction produces strain in all three directions as described by Hookes law and Poissons ratio ν.
KY3 1-2sigma Here K is bulk modulus and Y is young modulus where sigma represents poissons ratio. The theory of isotropic linear elasticity allows Poissons ratios in the range from -1 to 12 for an object with free surfaces with no constraint. 6 10 4 Nmm 2.
Modulus of rigidity η. The bulk modulus of the fluid in Equation 341 is the inverse of fluid compressibility. All three elastic constants can be interrelated by deriving a relation between them known as the Elastic constant formula.
Change in pressure δP 00 01. Bulk modulus K 120000 MPa. Delta P -01 MPa.
We have a mathematical relation between the Bulk modulusK and the Youngs modulusE is given by. Bulk modulus K. It is denoted by K or B.
8 10 4 Nmm 2. Hence the fractional change in. The Bulk modulus K of a material having Youngs Modulus E 200 GPa and Modulus.
It is defined as the ratio of normal stress to the volumetric strain within the elastic limit. 2 10 4 Nmm 2. N 3K - 2G 6K 2G E 2G 1 n E 3K 1 - 2 n Further interrelations among elastic constants for isotropic solids are as follows.
Bulk modulus K is the ratio of hydrostatic stress p on an object to the resulting volumetric strain ε v which is the ratio of volume change ΔV to the initial volume V o. Fractional change in volume. Hydrostatic stress cannot produce shear stress.
Youngs modulus is defined as the ratio of stress to strain. The bulk modulus is defined byaβpΔρρwhere p is the gauge pressure which causes the density change Δρ of a liquid whose density at p 0 is ρ. The bulk modulus of the material of the object is 120000 MPa.
Its resistance to do so is quantified as the bulk modulus K also known as the modulus of compression.
Solved 4 The Bulk Modulus K Of A Substance Is A Measure Of Chegg Com
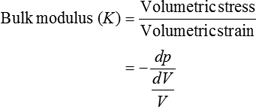
Definition Of Bulk Modulus Chegg Com
Applied Mechanics Of Solids A F Bower Chapter 3 Constitutive Laws 3 2 Linear Elasticity
What Is Bulk Modulus Bulk Modulus Vs Young S Modulus Vs Rigidity Modulus Extrudesign

Definition Of Bulk Modulus Elastic Constants Strength Of Materials Youtube

Calculated Elastic Constants C Ij Gpa Bulk Modulus B Gpa Shear Download Table